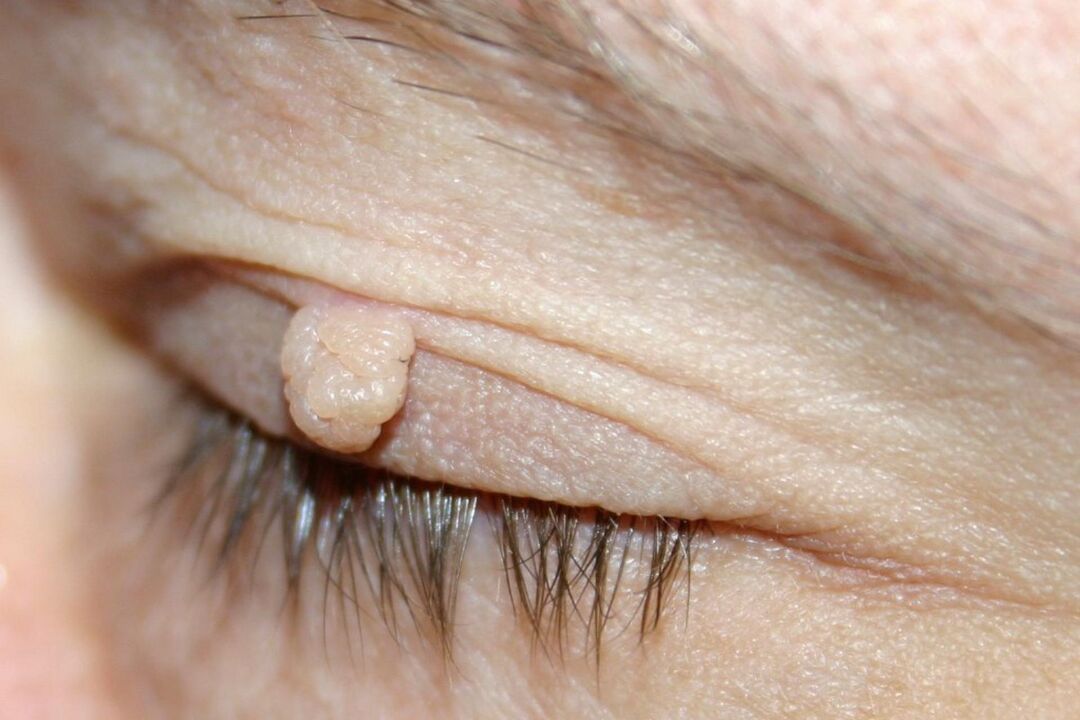
Papillomas of the eyelids- tumor-like neoplasms in the skin of the eyelid, as a result of infection with the human papillomavirus. Usually, papillomas appear only as a cosmetic defect; in some localizations, pain, sensation of a foreign body and other symptoms are possible. Visiometry, tonometry, refractometry, computerized perimetry, slit-lamp biomicroscopy are used for diagnosis. Of the additional methods, CT and biopsy are used, followed by histology of the material. Treatment of eyelid papilloma - removal of the tumor using chemical or physical methods of destruction. Prescription of antiviral drugs is mandatory.
General information
Papillomas of the eyelids are tumors of the integrative epithelium of the adnexal apparatus of the eye with varying degrees of dysplasia, caused by the human papillomavirus. Most often, eyelid papillomas are benign tumors, malignancy is rare. These neoplasms account for 60-65% of all eyelid neoplasms. More often (3. 5 cases per 100, 000 inhabitants) this pathology occurs in people living in equatorial countries. In Australia, the prevalence is 1. 9 cases per 100, 000 inhabitants. In countries with a temperate and subarctic climate, the disease is diagnosed less often. The category of patients is over 30 years old, the average age of patients ranges from 45-60 years. Women get sick one and a half times more often than men.
reason
The main etiological factor that provokes the development of papilloma of the eyelids is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). There are over 100 different types of papillomavirus. Human papillomavirus is tropic in the epidermis of the skin, it is transmitted by direct contact with the infected epithelium (more often there is family contact transmission, less often sexual). In addition, it can be transmitted from mother to fetus.
Factors that contribute to the development of eyelid papilloma include genetic predisposition, immunological and hormonal disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyper- or hypothyroidism, menopause), pregnancy, beriberi, frequent visits to the sunroom, cancer, smoking, alcohol consumption.
Pathogenesis
It is believed that in the basal layer there are cells sensitive to the papillomavirus and enough single particles of the virus to stimulate the development of eyelid papilloma. HPV is an obligate intracellular parasite that is usually present in the episomal form, d. m. th. , located in the cytoplasm of the cell. However, during reproduction, it can migrate into the nucleus (integration).
The beginning of integration (formation of papilloma of the eyelids) is possible even after 20 years from the beginning of the infection, the time of development of the disease is determined not only by the virus, but also by the presence of the patient's hereditary predisposition. in combination with other factors. Even while in the cytoplasm, the virus is able to produce intact viral particles. At this stage, the infection is often asymptomatic, highly contagious and can easily spread to other tissues and organs and cause eyelid papilloma.
The processes of virus reproduction, assembly of viral particles and their release from the cell have not been fully established. In a cell, the virus can exist simultaneously in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. When the virus enters the host organism, its cytoplasmic reproduction begins after penetrating the cells of the basal layer of the skin. In the stratum corneum, there is an active release of mature viral particles from the cells. These areas of the skin are dangerous in terms of contact infection.
Symptoms of eyelid papilloma
The clinical picture of papilloma of the eyelid depends on the location and the characteristics of the growth of education. Size, color, shape and growth pattern can vary greatly. Most often, papillomas are located on the lower eyelid and do not affect visual acuity. They are characteristic exophytic formations of gray to yellow color with papillary growth on the surface. In the center is a vascular loop.
Usually they are asymptomatic, the patient is referred to an ophthalmologist if an obvious cosmetic defect appears due to the growth of papilloma of the eyelids. When a neoplasm appears on the ciliary edge or on the border with the conjunctiva, the patient may complain of severe pain, foreign body sensation, blepharospasm, hyperemia and reduced vision. When blinking, the cornea is damaged by the uneven surface of the papilloma of the eyelid, which leads to the appearance of these symptoms.
Complications
Complications arise when the papilloma is located on the ciliary edge of the eyelids, in the intermarginal space, in the region of the inner corner of the eye, and also when the neoplasia spreads to the conjunctiva. It is characterized by the development of slow chronic conjunctivitis, blepharitis, corneal opacities. They can cause eyelash growth disorders, which leads to corneal microtrauma with the development of keratitis. The formation of ectropion causes the appearance of corneal erosion and ulcers, impaired visual function, up to atrophy of the eyeball. In addition, there is always the risk of malignancy of papilloma of the eyelids.
Diagnosing
The diagnosis of eyelid papilloma begins with a survey and visual examination of the patient by an ophthalmologist. Then the doctor uses standard examination methods: visiometer, tonometer, refractometer, computerized perimeter, slit-lamp biomicroscopy. Of the additional methods, if necessary, optical coherence tomography or computed tomography is used (assigned to multiple papillomas of different localizations), material is taken for a biopsy (using a trace, scratch or incision) followed by ahistological examination. In some cases, consultation with a dermatologist is necessary.
Treatment of eyelid papillomas
For the treatment of papilloma of the eyelids, chemical or physical methods of destroying the neoplasm are used. At the same time, antiviral drugs with immunomodulatory activity are prescribed. Destructive physical methods include removal of eyelid papilloma using electrocoagulation, laser therapy, cryotherapy (destruction of the neoplasm with liquid nitrogen). The chemical method is based on the use of various keratolytic agents. The choice of treatment option depends on the location and prevalence of the neoplasm, on the patient's age. The prognosis is often favorable.
prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at reducing the risk of infection with the human papillomavirus. Mandatory use of condoms during casual sex is recommended. If signs of HPV infection are detected, the examination of all the patient's sexual partners and the appointment of adequate treatment are required. To reduce the risk of eyelid papilloma formation, it is necessary to take measures to maintain immunity, do not touch the eyes with dirty hands, lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid excessive work and play activelysports. Refusal to visit the sunroom significantly reduces the risk of eyelid papilloma.














































































